mybatis源码分析之动态SQL语句分析
创建动态SQL
动态SQL作为mybatis最强大的功能之一,比起其他数据层的框架可以在开发中少很多麻烦,再也不用纠结多条件查询等问题了。在最新的mybatis版本,动态标签只有if、choose(when、otherwise)、trim(where、set)、foreach,同时动态标签中还可以使用OGNL表达式进行一些复杂的处理。mybatis生成SQL语句主要类之间的关系如下图所示:
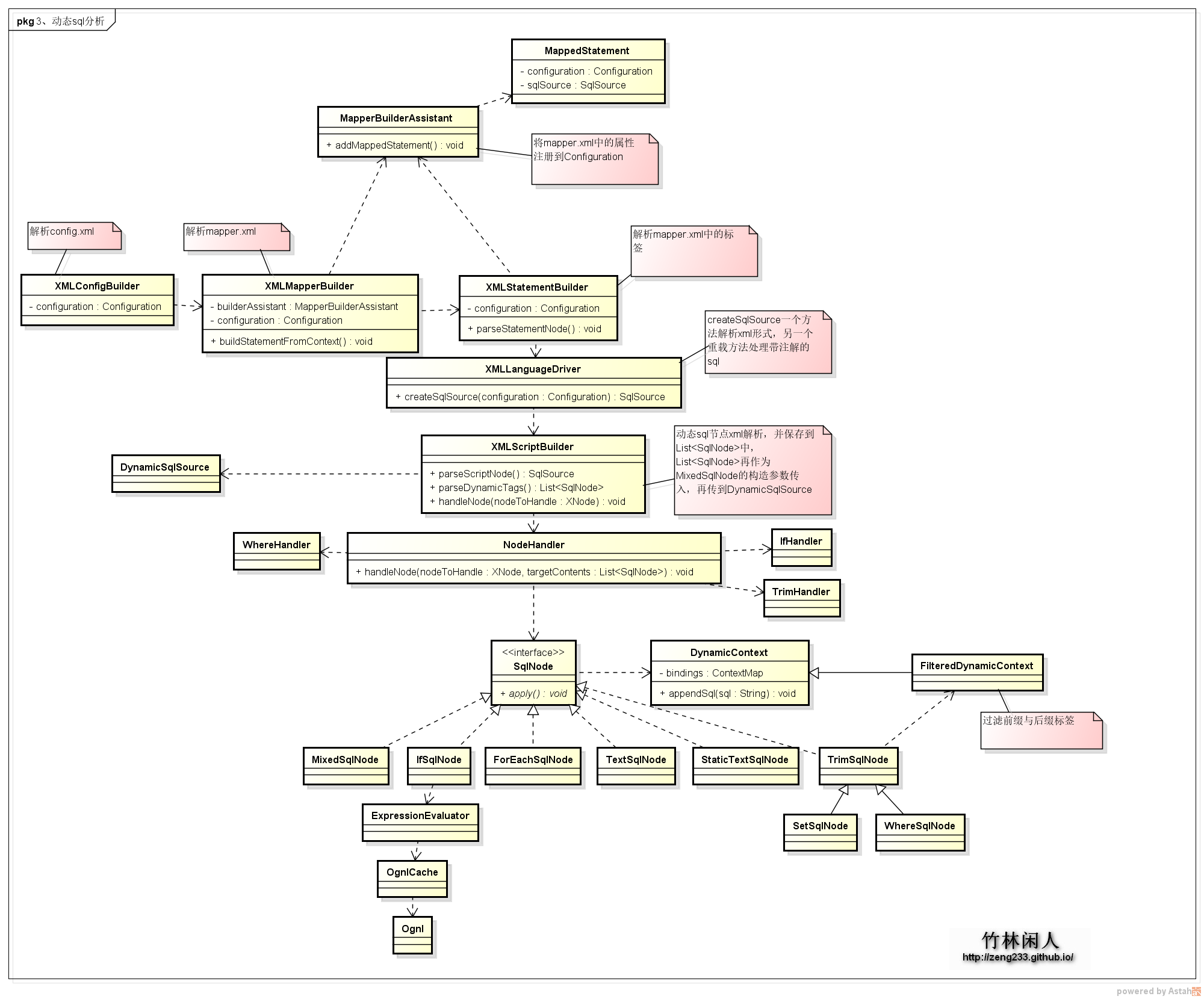
通过简单的一条查询语句跟踪,构建动态sql语句大概类之间的依赖关系就差不多明白了。
以动态查询SQL为例分析:
解析xml中的sql标签
XMLStatementBuilder专门解析mapper.xml文件中的sql语句标签,然后再把这条语句的MappedStatement对象添加到Configuration对象中去。 根据标签中的lang属性,可以用不同的语言去解析sql语句,可以为xml、注解、自定义velocity或者自定义freemarker解析等等。这里以xml为例,解析sql标签中的sql语句,又有个XMLScriptBuilder来处理,把sql语句中的标签处理完了,一条完整的sql就出来了。
根据传入的XNode(sql语句)节点,循环解析XNode的子节点,如果是文本就直接生成StaticTextSqlNode然后传到List
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
List<SqlNode> contents = parseDynamicTags(context);
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = new MixedSqlNode(contents);
SqlSource sqlSource = null;
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}这样就获取到DynamicSqlSource了,然后DynamicSqlSource作为参数传递到MappedStatement。
参考XMLStatementBuilder的parseStatementNode方法:
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);初始化BoundSql
解析动态sql语句的时候,只是把标签去除掉了,#{}表达式还是一样在sql语句里面的,这样显然不能执行。mybatis执行器执行sql语句首先从MappedStatement拿到上次构建的动态sql,参考MappedStatement.getBoundSql(),如图所示:
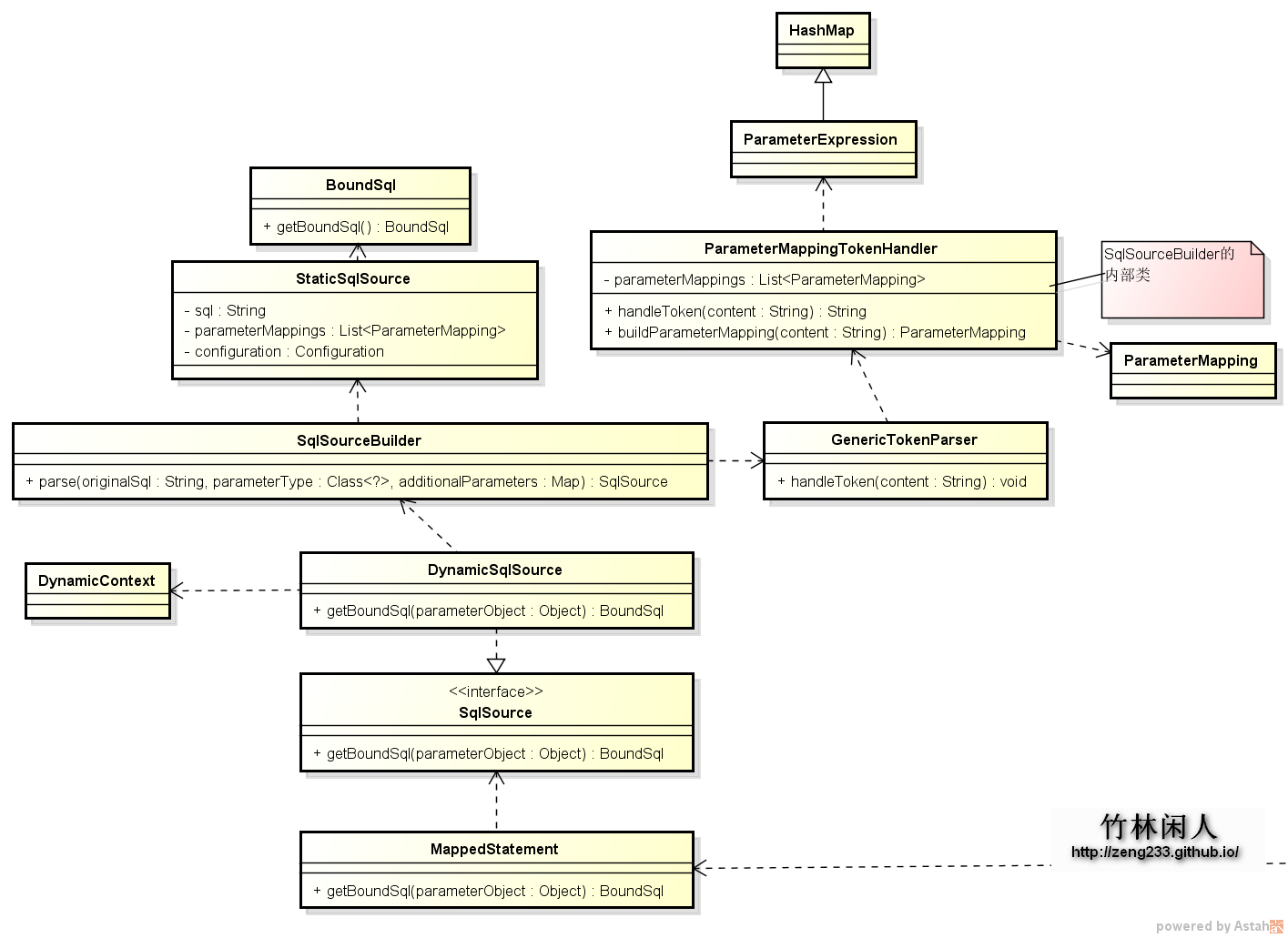
直接从DynamicSqlSource入手分析,DynamicSqlSource.getBoundSql(Object parameterObject)方法依赖两个重要的类:
1)DynamicContext:保存参数以及拼接SQL语句,ContextMap保存参数,里面使用了MetaObject(防止参数对象里面没有get\set方法)
2)SqlSourceBuilder:处理处理占位符和参数
3)ParameterMappingTokenHandler:SqlSourceBuilder的内部类,通过工具类GenericTokenParser的解析,构建参数对象ParameterMapping并保存到List列表parameterMappings中,然后将SQL语句中的占位符替换成问号(?)
4)StaticSqlSource:动态语句解析后的SqlSource,通过getBoundSql(Object parameterObject)获取到BoundSql
最终生成带?占位符的SQL语句。
针对sql标签中,当个参数时,没有参数标签(如parameterType),只能使用_parameter的原因:
判断if标签使用了OGNL表达式,因为实例化DynamicContext的时候,会将参数装进Map里面,默认的键值就为_parameter,在基本类型对象中没有get/set方法获取不到值,然后就去Map中去找key,如果有key值和这个参数对应,就可以继续拼接SQL了,#{_parameter}或者#{id}作为占位符都可以,但是
执行SQL语句
参考SimpleExecutor的prepareStatement方法:
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
log.debug("statemet:获取connection连接,如果要打印日志,则返回代理类ConnectionLogger");
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
log.debug("statement:参数化把占位符替换成具体值");
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}因为是动态SQL,会调用PreparedStatementHandler.parameterize方法,最后由DefaultParameterHandler处理带?的占位符,参考setParameters方法:
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
log.debug("parameter:解析bandSql中的参数并设置到PreparedStatement");
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {//如果参数类型在typeHandlerRegistry中能找到,就赋值给value
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
log.debug("parametor:这里就是执行类似于自定义自己的typehandler进行参数设置");
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
}
}
}
}typeHandler.setParameter就是专门处理传入的参数,然后由setNonNullParameter方法将参数值设置到PreparedStatement,这样最终生成的SQL就带?占位符,出入到PreparedStatement就可以执行了。