mybatis源码分析之执行器分析
不管mybatis还是其他开源项目,只要了解到它的执行流程,再分步骤看代码,思路就变得清晰多了。因为查询要稍微复杂点,就已查询流程为例进行分析。mybatis其实就分两大步骤,第一初始化解析XML,第二执行SQL, 执行器的整个执行的步骤大概如下:
SqlSessionFactory->Configuration->InterceptorChain->executor这个过程初始化executor,session->executor->cache->executor->interceptorChain->statementhandler(BaseStatementHandler构造函数时,新建ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler,要经过interceptorChain过滤)->resultset,类之间的依赖关系如下:

执行的时候会先从一级缓存里面去判断是否有值,然后再确定是否重新去数据库查询。再看源代码结构
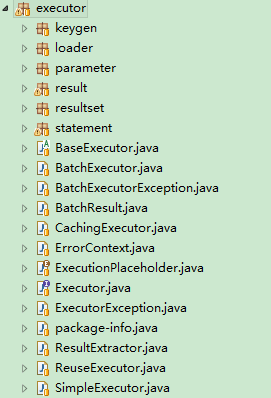
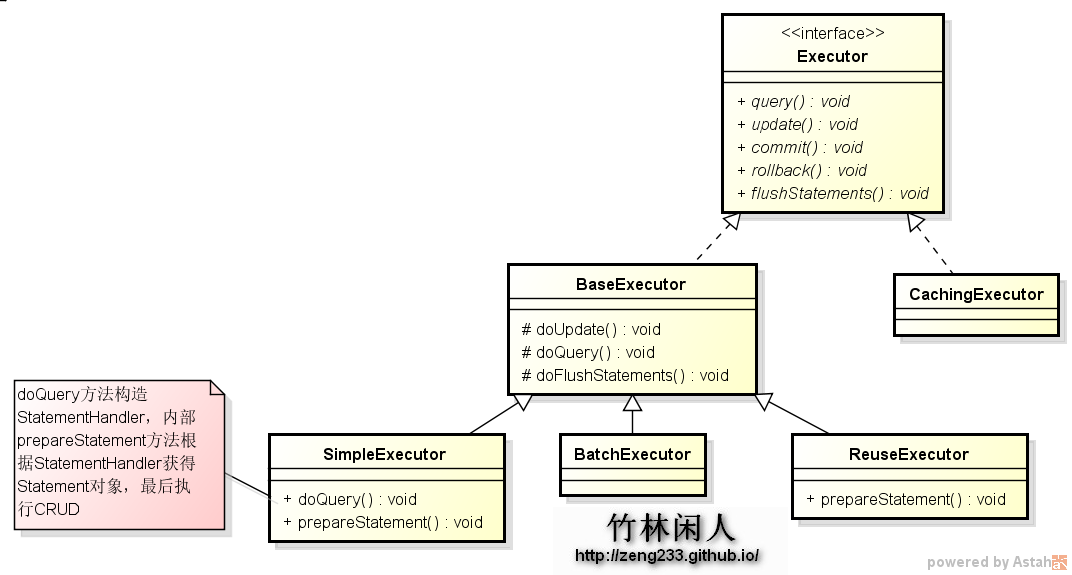
从包中的类也可以看出,executor中的类是最多的,算是最核心的模块了,因为通过执行器才能起到承上启下的作用。执行器的继承关系如下图所示:
Configuration创建executor的时候,参考源代码:
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
log.debug("新建默认执行器,传递configuration对象");
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
//装饰器模式应用,实际动作由SimpleExecutor执行
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}如果配置文件中没有设置是否启用缓存,mybatis默认就启用缓存执行器CachingExecutor。CachingExecutor与SimpleExecutor的最大的区别就是多了一个二级缓存,mapper.xml里面如果没有配置缓存,那么这两个执行器都会使用一级缓存,实例化CachingExecutor函数时,传了SimpleExecutor进去, 其实最终的查询都由SimpleExecutor去执行。参考BaseExecutor代码:
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
log.debug("executor:获取执行的BoundSQL");
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
log.debug("执行查询先从localCache查看是否有缓存");
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}默认就会启用PerpetualCache本地缓存,查看PerpetualCache,其实里面就一个HashMap来缓存结果集,缓存后面会单独分析,这里就不深入研究了。
执行器创建完成后,SimpleExecutor底层就由Statement去执行了,和JDBC差不多,设置参数,然后处理结果集了,获取Statement时,这里的设计和Executor几乎差不多的:
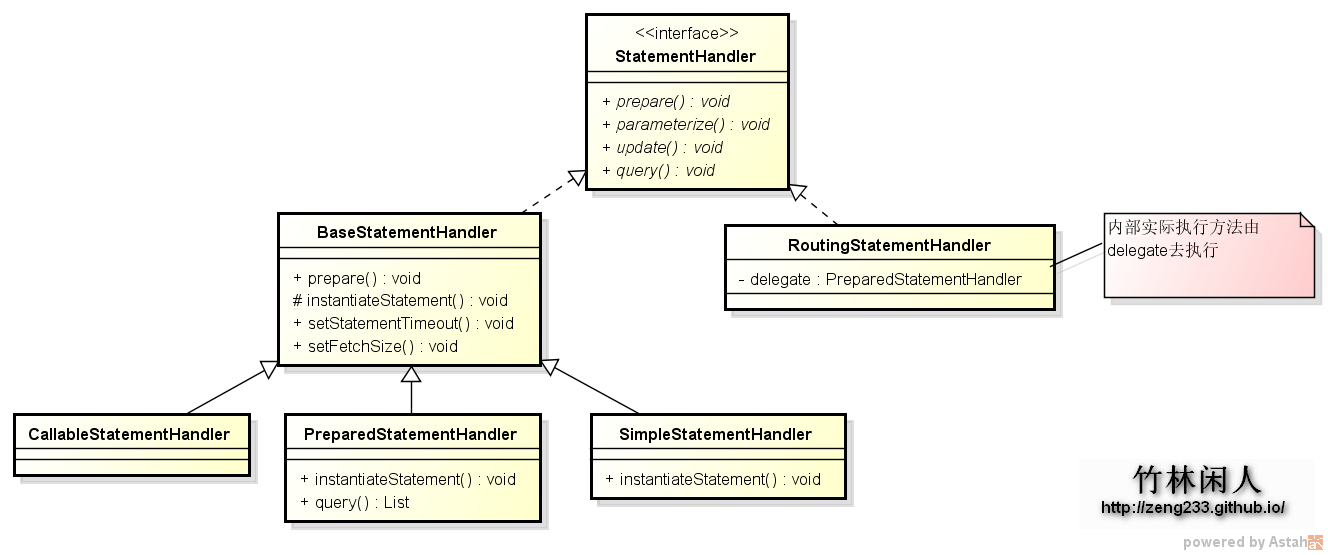
SimpleExecutor在获取Statement之前会先判断静态处理类型、预处理类型还是存储过程,参考Configuration的newStatementHandler方法:
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
log.debug("statement:新建RoutingStatementHandler");
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}实例化RoutingStatementHandler时,就判断是哪种类型,参考源代码:
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
log.debug("statement:实例化时,从MappedStatement对象判断并分发StatementHandler, 默认为StatementType.PREPARED");
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}如果是预处理的Statement,就实例化PreparedStatementHandler,由于与statement打交道离不开参数与结果集,所以抽象类
BaseStatementHandler里面就构造了参数、结果集类的句柄类,代码如下:
protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
this.executor = executor;
this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this.rowBounds = rowBounds;
this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory();
if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement
generateKeys(parameterObject);
boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
this.boundSql = boundSql;
log.debug("handler:初始化解析参数的parameterHandler,执行方法的sql参数传递");
this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
log.debug("handler:初始化结果集处理句柄ResultSetHandler");
this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql);
}经过判断是哪种Statement之后,SimpleExecutor的prepareStatement方法就开始实例化Statement了,与JDBC步骤差不多,要获取Statement,就
先要获取到Connection,在最开始实例化Executor就把transaction传进来了,通过transaction.getConnection();就获取到连接了,然后就通过句柄类StatementHandler的prepare实例化Statement,最后通过Statement或者PreparedStatement执行SQL语句了。参考SimpleExecutor:
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
log.debug("executor: 执行doQuery前新建分发的执行器");
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
log.debug("statement:实例化statement");
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
log.debug("executor:真正执行查询");
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}PreparedStatementHandler的执行:
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
log.debug("statemnt:执行结果集处理");
return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps);
}执行完语句客户端最后关闭连接sqlSession.close(),整个执行流程就基本清楚了,后面单独分析如何处理ResultMap,官方文档上面也说了,这个功能很强大,但是也很复杂,参考Result Map分析。